The greater auricular nerve plays an important role in innervating the skin of the ear and surrounding areas. Understanding its origins, anatomy, function, and clinical significance can provide valuable insights into various aspects of medical and surgical practice. In this article, we will explore these topics in depth, shedding light on the remarkable intricacies of this nerve.
Understanding the Greater Auricular Nerve
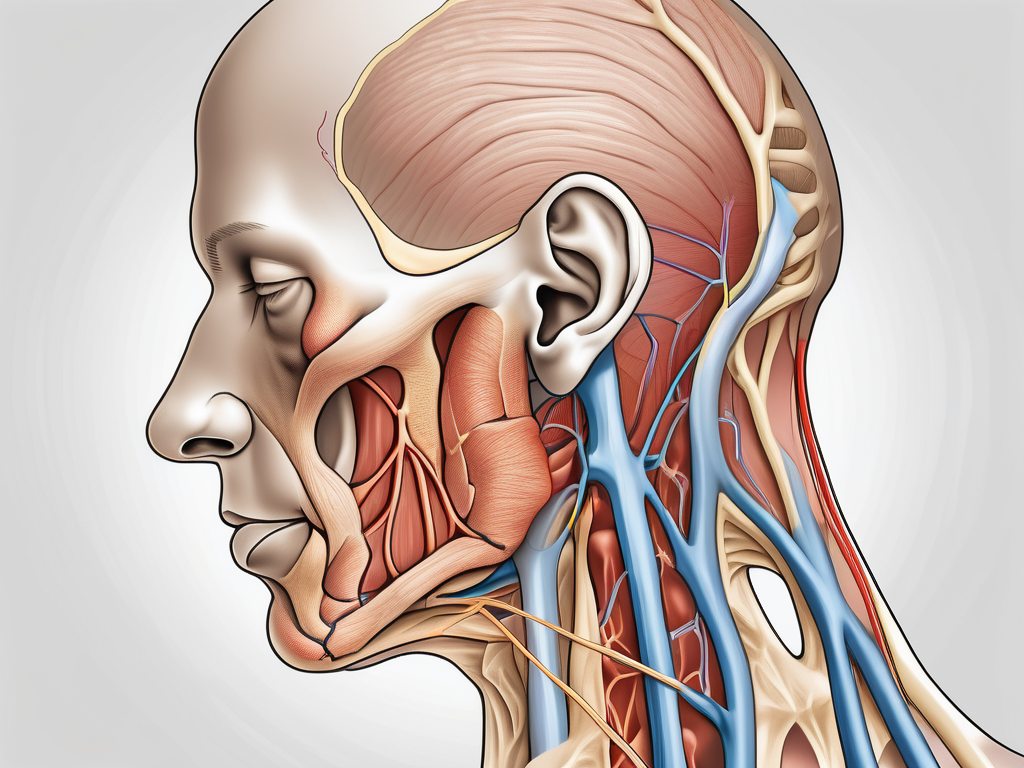
The greater auricular nerve, as its name suggests, supplies sensation to the auricle, or external ear. This essential nerve arises from the cervical plexus, a network of nerves that originate from the upper spinal cord. By tracing the pathway of the greater auricular nerve, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of its origin and function.
The cervical plexus is a complex network of nerves that plays a crucial role in the innervation of the head and neck region. It consists of branches from the upper spinal cord, specifically the second and third cervical nerves, known as C2 and C3. These nerves give rise to the greater auricular nerve, among others, which is responsible for providing sensory information to the auricle.
As the greater auricular nerve emerges from the cervical plexus, it embarks on a fascinating journey through the neck. It travels upwards and courses over the sternocleidomastoid muscle, an important landmark on the side of the neck. This muscle, named for its attachments to the sternum, clavicle, and mastoid process, serves as a guide for the greater auricular nerve as it makes its way towards its target.
Upon reaching the external ear, the greater auricular nerve divides into multiple branches that spread over the auricle and adjacent skin. This intricate branching pattern ensures that the entire external ear is supplied with sensory innervation, allowing us to perceive touch, pain, and temperature sensations in this region.
Anatomy of the Greater Auricular Nerve
The anatomy of the greater auricular nerve is a testament to the intricacy and precision of the human nervous system. Its origin from the cervical plexus and its pathway over the sternocleidomastoid muscle demonstrate the remarkable organization and coordination of nerves within the body.
As the greater auricular nerve courses over the sternocleidomastoid muscle, it follows a distinct pattern, highlighting the meticulous arrangement of nerve fibers. This pattern ensures that the sensory information from the auricle and surrounding skin is efficiently transmitted to the brain for processing and interpretation.
Understanding the anatomy of the greater auricular nerve is not only fascinating from a scientific standpoint but also crucial for medical professionals. Knowledge of this nerve’s pathway and branching pattern is essential in diagnosing and treating conditions that may affect its function, such as trauma or compression.
Function of the Greater Auricular Nerve
The primary function of the greater auricular nerve is to transmit sensory information from the skin of the auricle and the surrounding region. This includes pain, touch, and temperature sensations. The nerve fibers responsible for these sensations travel back to the brain, allowing us to perceive stimuli and respond accordingly.
Our ability to feel pain, detect touch, and sense temperature changes in the auricle is made possible by the intricate network of nerve fibers within the greater auricular nerve. These fibers carry signals from the skin to the brain, where they are processed and interpreted, enabling us to react appropriately to our environment.
The importance of the greater auricular nerve in our daily lives cannot be overstated. It allows us to enjoy the sensation of a gentle breeze on our ears, to protect ourselves from potential harm by feeling pain, and to respond to changes in temperature. Without the proper functioning of this nerve, our perception of the world around us would be significantly altered.
The intricate interaction between the greater auricular nerve and the brain reinforces the importance of maintaining its health and function. Any damage to this nerve can lead to various detrimental consequences, underscoring the need for vigilance in medical and surgical procedures. The delicate nature of the greater auricular nerve reminds us of the intricate balance that exists within our bodies and the importance of preserving and protecting our nervous system.
Origin of the Greater Auricular Nerve
As mentioned earlier, the greater auricular nerve arises from the cervical plexus, a crucial network of nerves in the neck region. Let us delve into the details of this connection and unravel the origins of this remarkable nerve.
The cervical plexus comprises a network of nerves that originate from the ventral rami of the upper four cervical spinal nerves (C1-C4). These nerves come together to form the plexus, which gives rise to various cutaneous and muscular branches, including the robust greater auricular nerve.
The intricate interplay between the cervical plexus and the greater auricular nerve highlights the importance of this nerve in conveying vital sensory information, serving as a conduit for essential neurological functions.
The greater auricular nerve, being one of the branches of the cervical plexus, plays a significant role in innervating the skin of the auricle and the surrounding areas. Its origin from the cervical plexus ensures that it receives sensory information from the upper cervical spinal nerves, allowing it to contribute to the overall sensory perception of the head and neck region.
Moreover, the cervical plexus itself has an interesting anatomical arrangement. It is formed by the merging of the ventral rami of the upper four cervical spinal nerves, which then give rise to various branches that supply different regions of the neck and head. This intricate network of nerves ensures the proper functioning of the sensory and motor systems in these areas.
Pathway of the Greater Auricular Nerve
After its origin from the cervical plexus, the greater auricular nerve follows a distinct pathway to innervate the skin of the auricle and the surrounding areas. The nerve travels superficially over the sternocleidomastoid muscle, emphasizing its proximity to the surface.
The pathway of the greater auricular nerve is not only anatomically fascinating but also clinically significant. Its superficial course allows for easier accessibility during diagnostic procedures and interventions. Healthcare providers can accurately locate and assess the integrity of the nerve by palpating its pathway, aiding in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of conditions affecting the nerve.
Furthermore, understanding the pathway of the greater auricular nerve helps healthcare professionals anticipate potential complications during surgical procedures or interventions in the head and neck region. By having a comprehensive knowledge of the nerve’s course, they can take appropriate precautions to minimize the risk of nerve damage and ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Clinical Significance of the Greater Auricular Nerve
The greater auricular nerve plays an essential role in both surgical procedures and the diagnosis of nerve damage and disorders. In this section, we will explore the clinical implications of the greater auricular nerve, highlighting its significance in the field of medicine.
Role in Surgical Procedures
Surgeons often encounter the greater auricular nerve during procedures involving the neck and adjacent regions. Its superficial location renders it susceptible to injury, making it crucial for surgeons to exercise caution and expertise to preserve nerve function.
Moreover, healthcare professionals rely on the greater auricular nerve as a landmark and guide during surgeries, allowing for precise dissection and surgical planning. Its role in surgical procedures underscores the importance of understanding its anatomy and function.
Implications in Nerve Damage and Disorders
Damage to the greater auricular nerve can occur due to trauma, inflammation, or compression. Nerve damage can manifest as altered or diminished sensations in the auricle or surrounding skin, leading to pain, numbness, or tingling.
If you are experiencing any concerning symptoms related to the greater auricular nerve, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, perform appropriate diagnostic tests, and recommend suitable treatment options.
Research and Discoveries about the Greater Auricular Nerve
The field of medical research continues to unravel fascinating findings about the greater auricular nerve. These discoveries contribute to our knowledge and pave the way for advancements in various areas of healthcare. Let us explore some recent findings and potential future directions in greater auricular nerve research.
Recent Findings on the Greater Auricular Nerve
In recent years, researchers have made significant strides in understanding the greater auricular nerve, shedding light on its intricate structure, function, and potential clinical applications. Studies have explored its role in pain management, nerve regeneration, and surgical techniques.
These discoveries hold promise for enhancing patient care and improving outcomes in medical and surgical interventions involving the greater auricular nerve.
Future Directions in Greater Auricular Nerve Research
The future of greater auricular nerve research lies in further unraveling its complexities and exploring its potential applications in the field of regenerative medicine. Researchers are investigating innovative techniques for nerve repair and reconstruction, aiming to restore function and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by nerve damage.
As the understanding of the greater auricular nerve deepens, healthcare providers can look forward to more targeted treatments and advancements in patient care.
Conclusion: The Importance of the Greater Auricular Nerve
The greater auricular nerve, originating from the cervical plexus, serves a critical role in innervating the skin of the auricle and the surrounding areas. Its anatomy, function, and clinical significance have profound implications in medical and surgical practice, warranting careful attention from healthcare professionals.
While further research and discoveries are on the horizon, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider if you have any concerns related to the greater auricular nerve. Your doctor can provide specialized guidance, diagnosis, and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
By prioritizing the health and function of the greater auricular nerve, we ensure optimal care for patients and pave the way for advancements in the field of neurology and surgical practice.
Leave a Reply