The posterior auricular nerve, also known as the great auricular nerve, plays a crucial role in the sensation and functionality of the ear and the surrounding area. However, like any other nerve in the body, it can become entrapped or compressed, leading to various symptoms and discomfort. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for posterior auricular nerve entrapment to provide a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
What is Posterior Auricular Nerve Entrapment?
Before we explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments of posterior auricular nerve entrapment, let’s define what nerve entrapment actually is. Nerve entrapment occurs when a nerve becomes compressed or irritated, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness. In the case of the posterior auricular nerve, when it becomes entrapped, it can cause various issues in the surrounding area, such as the scalp, the area behind the ear, and the upper neck.
Defining Nerve Entrapment
Nerve entrapment, also known as nerve compression or pinched nerve, is a condition in which a nerve in the body is compressed or squeezed, leading to discomfort and other problematic symptoms. This compression can occur due to physical trauma, inflammation, or even degenerative changes in the body.
When a nerve is entrapped, it can disrupt the normal flow of signals between the brain and the affected area. This disruption can result in a range of symptoms, depending on the specific nerve involved and the severity of the entrapment. Common symptoms include pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected area.
There are various factors that can contribute to nerve entrapment. Physical trauma, such as a direct blow or repetitive stress on a particular area, can lead to compression of the nerve. Inflammation caused by conditions like arthritis or tendonitis can also contribute to nerve entrapment. Additionally, degenerative changes in the body, such as herniated discs or bone spurs, can put pressure on the nerves, leading to entrapment.
The Role of the Posterior Auricular Nerve
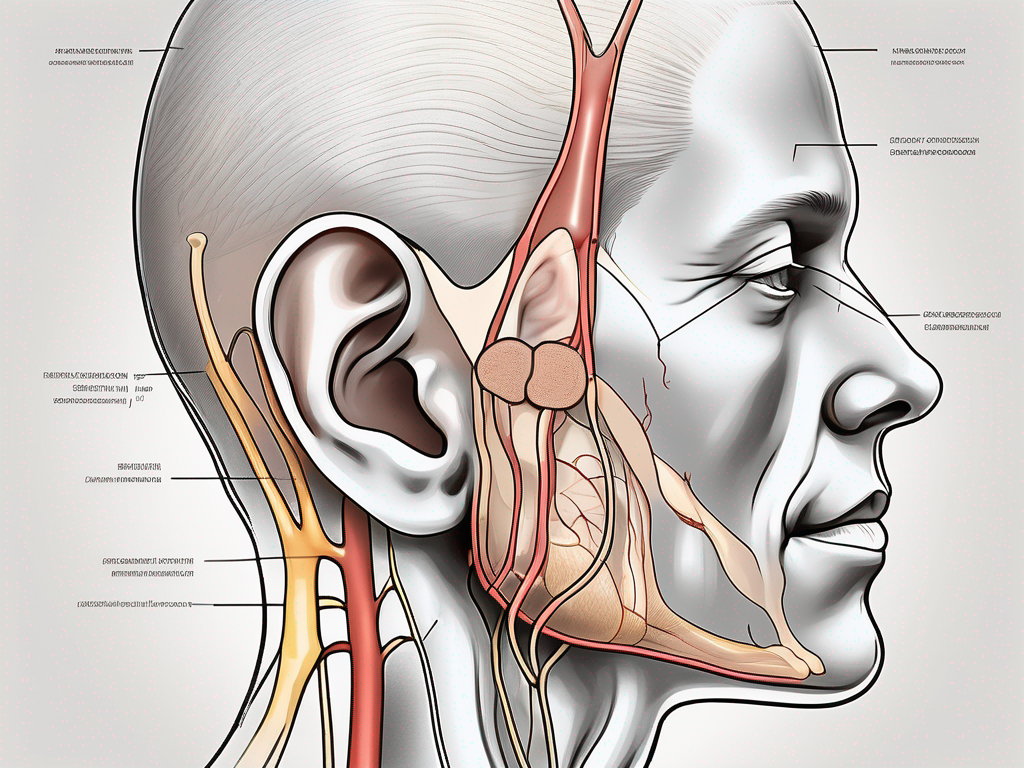
The posterior auricular nerve originates from the cervical plexus and has an important role in providing sensory innervation to the back of the ear, the scalp, and the angle of the mandible. It also contributes to the discomfort and symptoms that can occur when the nerve becomes entrapped.
When the posterior auricular nerve is entrapped, it can cause a variety of symptoms in the affected areas. Pain and tenderness may be felt behind the ear and along the scalp. Numbness or tingling sensations can also occur, making the affected area feel abnormal or “asleep.” In some cases, weakness in the muscles innervated by the posterior auricular nerve may be experienced, affecting movements of the head and neck.
Posterior auricular nerve entrapment can be caused by various factors. Trauma to the head or neck, such as a car accident or a fall, can lead to compression of the nerve. Repetitive motions or prolonged pressure on the area, such as frequently wearing tight headbands or helmets, can also contribute to entrapment. Additionally, inflammation in the surrounding tissues, such as from an infection or an autoimmune condition, can irritate the nerve and lead to entrapment.
It is important to diagnose and treat posterior auricular nerve entrapment promptly to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications. Treatment options may include conservative measures such as rest, physical therapy, and pain management techniques. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to release the entrapped nerve and restore normal function.
In conclusion, posterior auricular nerve entrapment is a condition in which the posterior auricular nerve becomes compressed or irritated, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the surrounding areas. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition can help individuals seek appropriate care and find relief from their symptoms.
Causes of Posterior Auricular Nerve Entrapment
Posterior auricular nerve entrapment can have various causes, ranging from physical trauma to underlying medical conditions. Understanding these causes can help in identifying and addressing the root of the problem.
When it comes to physical trauma and injury, there are several ways in which the posterior auricular nerve can become entrapped. Injuries to the head, neck, or ear region, such as falls, direct blows, or accidents, can lead to posterior auricular nerve entrapment. The trauma can cause swelling, inflammation, or direct pressure on the nerve, resulting in symptoms of entrapment. It is important to note that even seemingly minor injuries can have a significant impact on the nerve, so it is crucial to seek medical attention if any symptoms arise.
In addition to physical trauma, certain medical conditions can also contribute to posterior auricular nerve entrapment. Conditions such as cervical disc herniation, tumors, arthritis, or infections in the neck area can all lead to nerve entrapment. These conditions can cause structural changes or inflammation in the surrounding tissues, which can lead to nerve compression. It is important for individuals with these conditions to be aware of the potential risk and take appropriate measures to prevent nerve entrapment.
Aside from physical trauma and medical conditions, lifestyle factors can also play a role in posterior auricular nerve entrapment. Factors such as poor posture, repetitive movements, or prolonged periods of neck flexion can put unnecessary strain on the muscles and tissues in the neck, increasing the risk of nerve compression. It is important to maintain good posture and take regular breaks from activities that involve repetitive neck movements to reduce the risk of nerve entrapment.
Overall, posterior auricular nerve entrapment can have various causes, and it is important to consider all potential factors when diagnosing and treating the condition. Whether it is physical trauma, underlying medical conditions, or lifestyle factors, identifying the root cause can help in developing an effective treatment plan and preventing future occurrences of nerve entrapment.
Identifying Symptoms of Posterior Auricular Nerve Entrapment
Recognizing the symptoms of posterior auricular nerve entrapment is crucial in seeking appropriate medical attention and receiving timely treatment. The symptoms can vary from person to person, and they may include:
Physical Symptoms and Discomfort
Individuals with posterior auricular nerve entrapment may experience pain or tenderness in the area behind the ear or along the scalp. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be described as sharp, shooting, or throbbing. The discomfort can be constant or intermittent, depending on the underlying cause of the entrapment.
In addition to pain, some individuals may also notice muscle weakness in the affected area. This weakness can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as lifting objects or turning the head. Limited range of motion is another common physical symptom of posterior auricular nerve entrapment. Individuals may find it challenging to move their head or neck in certain directions without experiencing pain or discomfort.
Furthermore, a feeling of fullness in the affected area is often reported. This sensation can be likened to having a heavy or swollen feeling behind the ear or along the scalp. It may be accompanied by a sense of pressure or tightness.
Neurological Indicators
In some cases, nerve entrapment can also lead to neurological symptoms, such as numbness, tingling, or a pins-and-needles sensation in the ear, scalp, or neck region. These sensations can be intermittent or persistent, depending on the severity of the entrapment and the duration of the compression on the nerve.
Individuals may experience numbness, which is a loss of sensation in the affected area. This can make it difficult to feel touch, temperature, or pain. Tingling, on the other hand, is described as a prickling or “pins-and-needles” sensation. It can be mild or intense and may occur spontaneously or in response to certain movements or positions.
Additionally, some individuals may notice a heightened sensitivity to touch or temperature changes in the affected area. This increased sensitivity, known as hyperesthesia, can cause even gentle touch or slight temperature variations to feel painful or uncomfortable.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect posterior auricular nerve entrapment, it is important to consult with a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis. They can perform a thorough evaluation and recommend appropriate diagnostic tests to confirm the entrapment and determine the underlying cause.
Early intervention is crucial in managing posterior auricular nerve entrapment. Prompt medical attention can help alleviate symptoms, prevent further nerve damage, and improve overall quality of life. Remember, each individual’s experience with nerve entrapment may vary, so it is essential to seek personalized medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options for Posterior Auricular Nerve Entrapment
Once posterior auricular nerve entrapment has been diagnosed, treatment options can be explored to alleviate symptoms and improve functionality. The choice of treatment will depend on the severity of the entrapment, the underlying cause, and individual factors.
Non-Surgical Treatments
In many cases, non-surgical approaches can effectively manage posterior auricular nerve entrapment. These may include physical therapy, pain management techniques, such as medications or nerve blocks, and lifestyle modifications. Your healthcare provider may also recommend exercises or stretches to improve muscle strength and flexibility in the affected area.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases of posterior auricular nerve entrapment or when conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. The surgical procedure aims to remove any compression or irritation on the nerve, allowing it to function properly. Surgical options can range from nerve decompression to the removal of any structural abnormalities or tumors causing the entrapment.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Following surgical intervention or non-surgical treatments, rehabilitation and recovery play a crucial role in restoring functionality and preventing further complications. Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises can aid in regaining strength, improving range of motion, and minimizing the risk of future nerve entrapment.
In conclusion, understanding posterior auricular nerve entrapment is vital in recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition. If you suspect you may be experiencing posterior auricular nerve entrapment, it is advisable to consult with a medical professional who can provide a comprehensive evaluation and guide you towards appropriate treatment options for your individual situation.
Leave a Reply