The great auricular nerve is a crucial component of the human nervous system that plays a significant role in various bodily functions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for inflammation of this nerve is essential for individuals experiencing related discomfort or seeking knowledge about this condition. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy, functions, and potential causes of great auricular nerve inflammation. We will also explore the common symptoms associated with this condition and discuss diagnostic procedures that can aid in its identification. Finally, we will provide an overview of the available treatment options, focusing on the importance of seeking medical advice for proper management.
What is the Great Auricular Nerve?
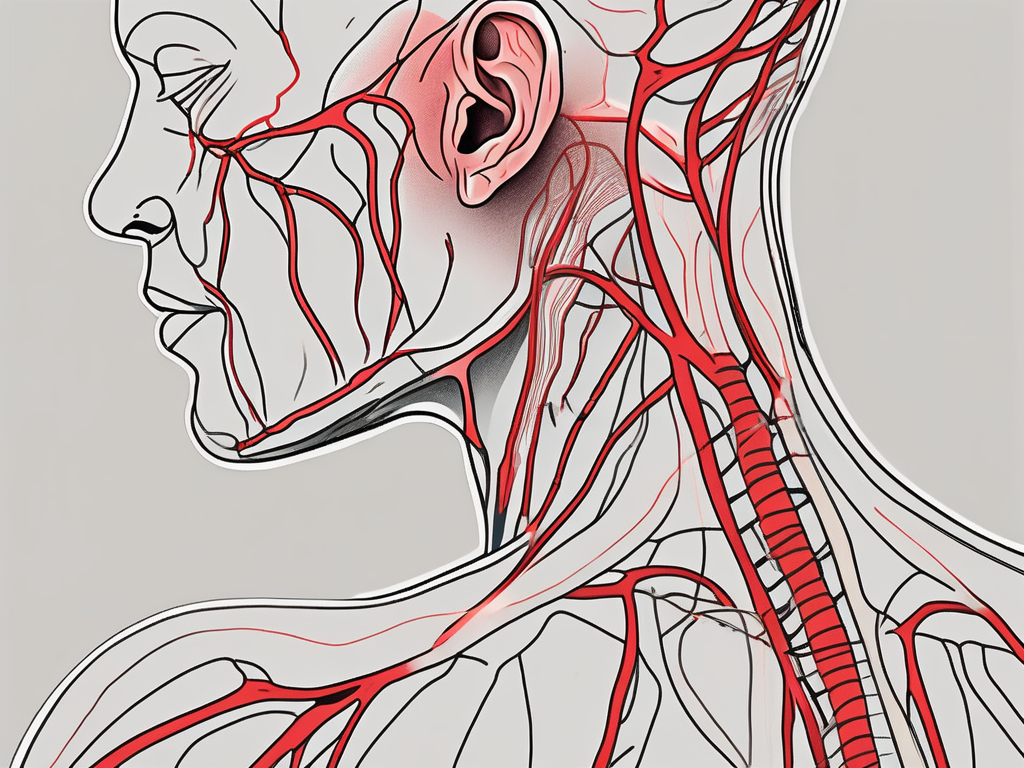
The great auricular nerve is a sensory branch of the cervical plexus, arising from the second and third cervical nerve roots (C2-C3). It courses superficially over the sternocleidomastoid muscle, extending towards the ear and the parotid gland. This nerve carries sensory fibers that provide innervation to the skin over the parotid gland, external ear, and mastoid region.
Anatomy of the Great Auricular Nerve
The great auricular nerve originates from the posterior aspect of the cervical plexus, emerging between the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the trapezius muscle. It ascends vertically towards the ear, branching into multiple smaller nerve endings along its course. These nerve endings penetrate the dermis of the skin overlying the parotid gland and the external ear.
As the great auricular nerve travels towards the ear, it forms connections with other nerves in the area. These connections allow for the integration of sensory information from different regions, ensuring a comprehensive perception of touch, pain, and temperature in the innervated areas.
Furthermore, the great auricular nerve exhibits anatomical variations among individuals. While the general trajectory and distribution of the nerve remain consistent within the population, the specific branching patterns and the number of nerve endings can differ. This variability highlights the complexity and adaptability of the nervous system.
Function of the Great Auricular Nerve
The primary function of the great auricular nerve is to provide sensory innervation to the areas it supplies, including the skin over the parotid gland, external ear, and mastoid region. Through its extensive network of nerve endings, the great auricular nerve enables the perception of various sensations, such as light touch, pressure, pain, and temperature.
In addition to its sensory role, the great auricular nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the reflex pathways involving the cervical spinal nerves. These reflex pathways allow for coordinated motor responses and sensations in the neck and shoulder regions. By relaying sensory information to the central nervous system, the great auricular nerve contributes to the smooth functioning of these reflexes, ensuring efficient and accurate responses to external stimuli.
Moreover, the great auricular nerve has been found to have connections with other cranial nerves, such as the facial nerve. These connections allow for the integration of sensory information between different regions of the head and neck, facilitating a comprehensive perception of the surrounding environment.
Overall, the great auricular nerve is a vital component of the sensory system, providing innervation to the skin over the parotid gland, external ear, and mastoid region. Its intricate anatomy and functional connections enable the perception of various sensations and contribute to the coordination of motor responses in the head and neck.
Understanding Nerve Inflammation
Nerve inflammation, also known as neuritis, refers to the irritation or swelling of a nerve. This condition can occur in any nerve within the body, leading to pain, sensory disturbances, and potential functional impairments.
General Causes of Nerve Inflammation
Nerve inflammation can arise from various factors, including viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune diseases, traumatic injuries, and certain metabolic conditions. In some cases, the exact cause may remain unknown.
It is important to emphasize that nerve inflammation is a complex condition, and its underlying causes can differ significantly depending on the affected nerve and the individual’s medical history. Therefore, consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management.
Impact of Inflammation on Nerve Function
When a nerve is inflamed, the normal functioning of its fibers can be compromised. The inflammation may disrupt the transmission of electrical impulses along the nerve, leading to altered sensations, weakness, or even paralysis.
Additionally, the surrounding tissues of an inflamed nerve may become hypersensitive, resulting in heightened pain perception. It is important to remember that nerve inflammation can have diverse manifestations depending on the specific nerve affected and the underlying cause.
Causes of Great Auricular Nerve Inflammation
Great auricular nerve inflammation can result from various factors, which primarily fall into two categories: infections and trauma.
Infections and Great Auricular Nerve Inflammation
Infections, particularly those caused by viruses or bacteria, can lead to inflammation of the great auricular nerve. Viral infections, such as herpes zoster (shingles), and bacterial infections, like cellulitis, can affect the nerve directly or indirectly through the surrounding tissues. Inflammation in these cases often manifests as redness, swelling, pain, and hypersensitivity in the region supplied by the great auricular nerve.
If you suspect an infection involving the great auricular nerve, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and appropriate treatment, which may include antiviral or antibiotic medications.
Trauma and Great Auricular Nerve Inflammation
Trauma, such as direct injury or compression of the great auricular nerve, can also result in inflammation. Accidental impact to the ear or neck, surgical procedures, or repetitive motion involving these regions can potentially damage the nerve, triggering the inflammatory response.
If you experience trauma involving the great auricular nerve or have persistent pain or discomfort in the corresponding area, seeking prompt medical evaluation is highly recommended to rule out any significant underlying injuries.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Great Auricular Nerve Inflammation
Great auricular nerve inflammation can present with various symptoms, both physical and sensory in nature. Understanding these manifestations is crucial for proper recognition and timely management.
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms associated with great auricular nerve inflammation may include redness, swelling, and tenderness in the region supplied by the affected nerve. Some individuals may also experience localized warmth or changes in skin texture, such as peeling or dryness.
It is important to note that these physical symptoms alone may not be sufficient for conclusive diagnosis, as they can also be indicative of other conditions. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough examination and accurate evaluation.
Sensory Symptoms
Great auricular nerve inflammation can lead to various sensory disturbances. These may include pain, tingling, numbness, or hypersensitivity in the region supplied by the nerve. Some individuals may experience a burning or prickling sensation, while others may report a decrease in sensation.
If you notice any unusual or persistent sensory symptoms in the areas supplied by the great auricular nerve, it is essential to seek medical advice for proper assessment and potential referral to a specialist, such as a neurologist or an otolaryngologist.
Diagnostic Procedures for Great Auricular Nerve Inflammation
Accurate diagnosis of great auricular nerve inflammation usually involves a combination of medical history assessment, thorough physical examination, and supportive tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination
During the medical history assessment, the healthcare professional will inquire about your symptoms, their duration, any recent infections or injuries, and relevant medical conditions. This information will aid in identifying potential triggers and narrowing down the diagnosis.
A comprehensive physical examination will focus on evaluating the affected region, assessing any physical signs of inflammation or trauma, and determining the extent of sensory disturbances. The examination may involve gentle palpation, temperature assessment, and sensory testing.
Imaging and Laboratory Tests
In some cases, the healthcare professional may recommend additional tests to support the diagnosis. These may include imaging studies, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to visualize the affected area and rule out other potential causes of symptoms.
Laboratory tests, such as blood work or fluid analysis, may be ordered to assess for signs of infection or inflammation. These tests can provide valuable information to guide the appropriate treatment plan.
It is essential to remember that the specific diagnostic procedures recommended may vary depending on the individual case and the healthcare professional’s judgment. Seeking timely medical evaluation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and further management.
Treatment Options for Great Auricular Nerve Inflammation
Treatment for great auricular nerve inflammation primarily aims to alleviate symptoms and address the underlying cause if identified. The treatment approach may differ based on factors such as the severity of symptoms, the suspected cause, and individual patient preferences.
Commonly employed treatment modalities may include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help manage mild pain and inflammation. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication. They may prescribe stronger analgesics or anti-inflammatory medications, depending on the severity of symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy sessions, including gentle stretching exercises and manual techniques, can help improve range of motion and reduce pain. A trained physical therapist can design an individualized rehabilitation program based on the specific needs of the patient.
- Local Measures: Applying warm compresses or cold packs to the affected area, as advised by a healthcare professional, may provide temporary relief from pain or swelling associated with great auricular nerve inflammation.
- Refraining from Triggering Activities: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as excessive neck rotation or contact sports, can help prevent further irritation of the inflamed nerve.
- Consultation with Specialists: In certain cases, referral to a specialist, such as a neurologist or pain management specialist, may be necessary for further evaluation and management. These specialists can offer specialized treatment modalities, such as nerve blocks or neurostimulation techniques, if appropriate.
It is important to highlight that the above treatment options are general suggestions and may vary depending on individual circumstances. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to tailor the treatment plan according to your specific needs and to monitor your progress.
In conclusion, understanding great auricular nerve inflammation is vital for individuals experiencing related symptoms or seeking information about this condition. By comprehending the causes, symptoms, and treatment options associated with this condition, individuals can seek appropriate medical advice and achieve the best possible outcomes. Remember, accurate diagnosis and management should be pursued with the guidance of healthcare professionals for optimal understanding and resolution of great auricular nerve inflammation.
Leave a Reply