Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation is a groundbreaking medical procedure that offers a range of benefits for patients suffering from various conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the science behind this innovative treatment, its procedure, and the potential health benefits it offers. However, it is essential to note that while this article provides valuable information, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you are considering Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine whether it is suitable for your specific condition. With that in mind, let’s delve into the fascinating world of Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation.
Understanding the Great Auricular Nerve
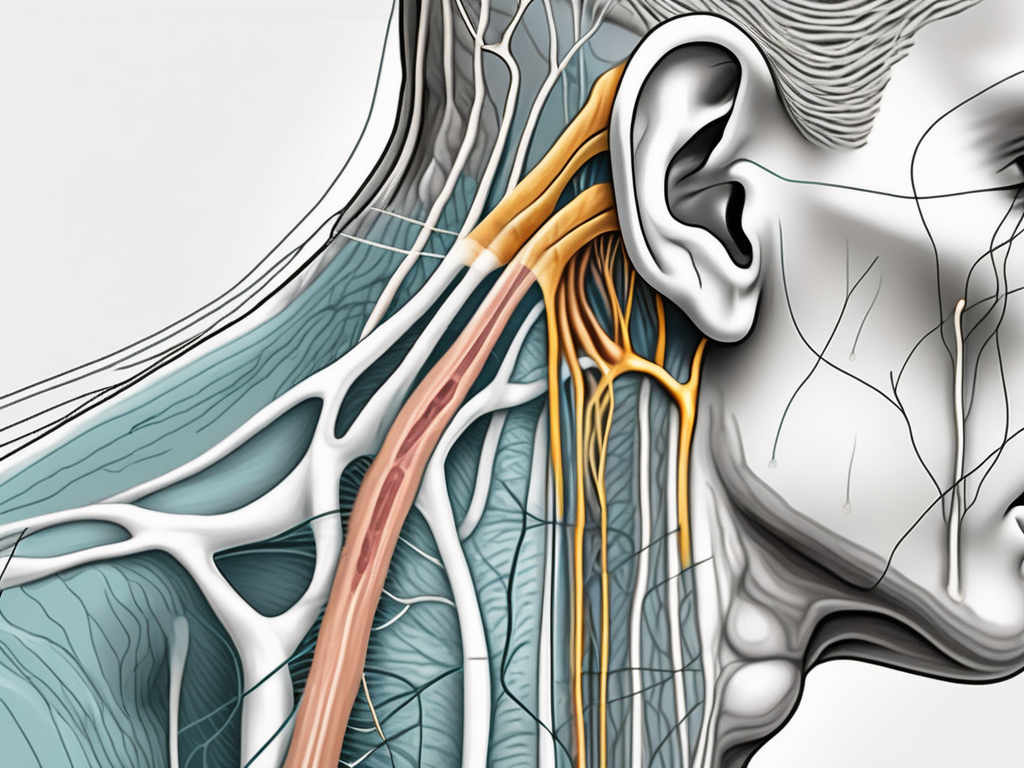
The Great Auricular Nerve, also known as the Auricular Branch of the Cervical Plexus, plays a crucial role in the sensory innervation of the ear and surrounding areas of the face and neck. This nerve originates from the second and third cervical spinal nerves and supplies sensation to the skin of the external ear, the area behind the ear, and the angle of the jaw.
The Great Auricular Nerve is a fascinating component of the human nervous system. Its intricate anatomy and specialized functions contribute to the overall sensory experience of the ear and its adjacent regions. Let’s delve deeper into the details of this remarkable nerve.
Anatomy of the Great Auricular Nerve
The Great Auricular Nerve is composed of sensory fibers and travels along a path that runs superficially through the subcutaneous tissue around the ear. It branches off from the cervical plexus and extends into the neck before making its way towards the ear.
As it courses through the subcutaneous tissue, the Great Auricular Nerve forms an intricate network of nerve fibers, intertwining with blood vessels and other structures. This intricate arrangement ensures the efficient transmission of sensory information from the ear to the central nervous system.
The nerve’s origin from the second and third cervical spinal nerves highlights its close association with the cervical plexus, a network of nerves that supplies various regions of the head and neck. This connection allows for coordinated sensory input and integration, ensuring optimal functioning of the ear and its surrounding areas.
Functions of the Great Auricular Nerve
The primary function of the Great Auricular Nerve is to provide sensory innervation to the designated areas. It enables the perception of touch, temperature, and pain in the external ear, helping to maintain proper sensation and function.
Additionally, the Great Auricular Nerve plays a crucial role in the regulation of blood flow to the ear. Through its intricate network of nerve fibers, it communicates with blood vessels, allowing for the adjustment of blood supply based on the body’s needs. This dynamic regulation ensures the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the ear, promoting its overall health and vitality.
Furthermore, the Great Auricular Nerve contributes to the body’s protective mechanisms. By providing sensory feedback, it alerts the individual to potential dangers or injuries in the ear and surrounding areas. This early warning system allows for quick reflexive responses, such as pulling away from a hot object or avoiding harmful stimuli.
In conclusion, the Great Auricular Nerve is a remarkable component of the human nervous system. Its intricate anatomy and specialized functions contribute to the overall sensory experience of the ear and its adjacent regions. Understanding the complexities of this nerve enhances our appreciation for the intricacies of the human body and its ability to perceive and respond to the world around us.
The Science Behind Nerve Stimulation
Nerve stimulation is a well-established medical practice that involves electrically activating specific nerves to alleviate pain or improve bodily functions. It is a fascinating field that has revolutionized the way we approach pain management and rehabilitation. In the case of Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation, this process involves the use of strategically placed electrodes that deliver mild electrical impulses to the nerve, triggering various physiological responses.
The Great Auricular Nerve, also known as the auricular branch of the vagus nerve, is a crucial nerve located in the neck region. It plays a significant role in providing sensory innervation to the skin of the ear, as well as the surrounding areas. By targeting this specific nerve, healthcare professionals can effectively address a range of conditions, including chronic pain, migraines, and even certain neurological disorders.
The Process of Nerve Stimulation
The procedure for Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation starts with the placement of electrodes near the Great Auricular Nerve area. The electrodes are carefully positioned to ensure optimal contact with the nerve fibers. The patient may be under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort during the process. Once the electrodes are in place, a small device, such as a neurostimulator, is utilized to emit controlled electrical signals to the nerve.
The neurostimulator is a remarkable piece of technology that allows healthcare professionals to precisely control the intensity and frequency of the electrical impulses. This customization ensures that the patient receives the most effective treatment tailored to their specific needs. The electrical signals generated by the neurostimulator travel through the electrodes and stimulate the Great Auricular Nerve, initiating a series of physiological responses.
It is important to note that nerve stimulation procedures are performed by trained medical professionals who have a deep understanding of the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system. They carefully assess each patient’s condition and determine the appropriate parameters for the electrical stimulation, ensuring both safety and efficacy.
The Impact of Nerve Stimulation on the Body
When the electrodes stimulate the Great Auricular Nerve, it initiates a cascade of reactions within the body. These reactions can modulate pain signals, promote blood circulation, and facilitate the release of certain neurotransmitters that aid in pain management and enhanced well-being.
One of the key effects of nerve stimulation is the modulation of pain signals. By delivering controlled electrical impulses to the nerve, the brain’s perception of pain can be altered. This can lead to a significant reduction in pain intensity and an improved quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions.
Additionally, nerve stimulation has been shown to promote blood circulation in the targeted area. The electrical impulses cause the blood vessels to dilate, increasing blood flow to the surrounding tissues. This enhanced circulation can facilitate the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the cells, promoting tissue healing and regeneration.
Furthermore, nerve stimulation can trigger the release of certain neurotransmitters, such as endorphins and serotonin, which are known to have analgesic and mood-enhancing effects. These neurotransmitters act as natural painkillers and can contribute to a sense of well-being and relaxation.
Overall, nerve stimulation is a remarkable technique that harnesses the power of electrical impulses to positively influence the body’s physiological processes. It offers a non-invasive and drug-free approach to pain management and functional improvement, providing hope and relief to countless individuals around the world.
Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation: An Overview
Now that we have covered the basics of the Great Auricular Nerve and nerve stimulation, let’s take a closer look at the procedure of Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation itself and the specialized tools and techniques involved.
The Procedure of Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation
The procedure typically begins with a thorough examination and assessment by a skilled healthcare professional. If the patient’s condition meets the criteria for Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation, the actual procedure can be scheduled. During the process, the patient is carefully monitored and supported by a professional medical team to ensure optimal safety and effectiveness.
Tools and Techniques Used in Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation
The tools and techniques employed in Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation have evolved significantly over time. Advanced imaging technologies, such as ultrasound, can assist in precise electrode placement, while modern neurostimulators offer better control and customization options for patients. These advancements contribute to increased accuracy and outcomes for individuals undergoing this procedure.
The Health Benefits of Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation
Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation has shown promising results in various areas of health and well-being. While it is important to emphasize that every individual’s response to the treatment can vary, let’s explore a few potential benefits that have been observed.
Pain Management and Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation
One notable area where Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation has shown promise is in pain management. By stimulating the nerve, the procedure can help alleviate chronic pain in the affected area, providing significant relief for individuals struggling with conditions such as trigeminal neuralgia or postoperative pain.
Mental Health and Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation
Additionally, preliminary studies suggest that Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation may have a positive impact on mental health conditions. While more research is needed in this area, early findings indicate potential benefits for individuals dealing with depression, anxiety, or even substance abuse disorders. However, it’s important to note that this procedure should not replace traditional mental health treatments, and a comprehensive approach should be taken when addressing these conditions.
Risks and Considerations of Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation
While Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation offers exciting possibilities, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and considerations associated with the procedure.
Potential Side Effects of Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation
Like any medical procedure, Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation carries the risk of side effects. These can include minor discomfort or swelling at the electrode site, infection, or unanticipated nerve responses. It is crucial to discuss these potential risks thoroughly with your healthcare professional before deciding on this treatment option.
Who Should Consider Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation?
Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation is a specialized procedure that should be carefully considered and discussed with a qualified healthcare professional. It may be an appropriate option for individuals experiencing chronic pain or certain neurological conditions. However, the eligibility for this treatment can vary depending on individual factors, and a comprehensive medical evaluation is necessary to determine its suitability for each patient.
In conclusion, Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation is a remarkable medical technique that holds significant potential for providing relief and improving quality of life. While this article has provided a comprehensive guide, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if this procedure is right for you. With ongoing advancements in medical research and technology, Great Auricular Nerve Stimulation continues to open new doors in the field of pain management and overall well-being.
Leave a Reply