The greater auricular nerve is an important nerve that plays a crucial role in the sensory innervation of the head and neck region. When this nerve becomes impinged or compressed, it can lead to a variety of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s daily life. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for impingement of the greater auricular nerve.
Understanding the Greater Auricular Nerve
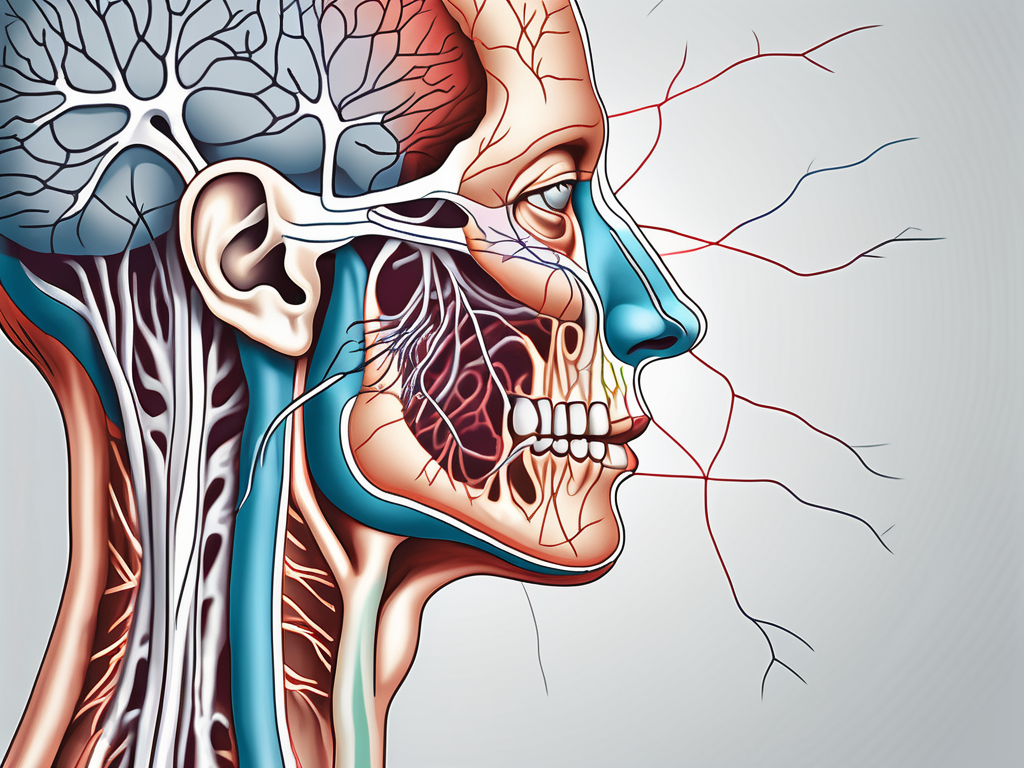
The greater auricular nerve is a branch of the cervical plexus, originating from the C2 and C3 spinal nerves. It runs superficially to the sternocleidomastoid muscle and then divides into multiple smaller branches that supply sensation to the skin overlying the ear and the mastoid process.
The greater auricular nerve plays a crucial role in the sensory innervation of the head and neck region. It is responsible for transmitting important sensory information from the lateral aspect of the head and neck to the brain, allowing us to perceive tactile sensations such as touch, temperature, and pain in these areas.
Anatomy of the Greater Auricular Nerve
The greater auricular nerve arises from the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, approximately at the level of the angle of the mandible. From there, it courses superiorly and anteriorly, dividing into several branches that supply sensation to the external ear and the adjacent skin.
As the nerve travels along its course, it closely accompanies the superficial temporal artery and the external jugular vein. This close proximity to these blood vessels not only provides the nerve with a source of nourishment but also contributes to its sensory function.
The branches of the greater auricular nerve extend to the skin overlying the ear, providing sensory innervation to this area. Additionally, these branches also supply sensation to the mastoid process, a bony prominence located behind the ear. This intricate network of nerve fibers ensures that the skin in these regions is adequately supplied with sensory information.
Furthermore, the greater auricular nerve sends branches to the parotid gland, a salivary gland located in front of the ear. These branches contribute to the innervation of the gland, allowing for proper functioning and regulation of saliva production.
Function of the Greater Auricular Nerve
The primary function of the greater auricular nerve is to transmit sensory information to the brain from the skin of the lateral head and neck region. It enables us to perceive tactile sensations, such as touch, temperature, and pain, in these areas.
When the skin overlying the ear or the mastoid process is stimulated, the nerve fibers of the greater auricular nerve are activated. These activated nerve fibers then transmit signals to the brain, allowing us to experience sensations such as the gentle touch of a breeze, the warmth of sunlight, or the pain from an injury.
In addition to its sensory function, the greater auricular nerve also plays a role in regulating blood flow in the head and neck region. The close association of the nerve with the superficial temporal artery and the external jugular vein allows it to influence the diameter of these blood vessels, thereby affecting blood flow and temperature regulation in the surrounding tissues.
Overall, the greater auricular nerve is a vital component of the sensory system in the head and neck. Its intricate anatomy and function contribute to our ability to perceive and interpret the world around us, making it an essential part of our daily lives.
Causes of Greater Auricular Nerve Impingement
There are several factors that can lead to impingement or compression of the greater auricular nerve. Understanding these causes is essential in the diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Physical Trauma and Injuries
Physical trauma, such as a direct blow or injury to the side of the head or neck, can result in compression of the greater auricular nerve. This can occur in various situations, including sports-related injuries, motor vehicle accidents, or falls.
It is important to seek immediate medical attention if you have experienced any head or neck trauma and are experiencing symptoms such as pain, numbness, or tingling in the affected area. A healthcare professional will be able to evaluate your condition and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options.
Medical Conditions Leading to Nerve Impingement
There are certain medical conditions that can contribute to impingement of the greater auricular nerve. For example, the presence of tumors, cysts, or infections in the head and neck region can cause compression of the nerve and lead to symptoms.
Other underlying medical conditions, such as cervical spine disorders or nerve entrapment syndromes, can also be associated with nerve impingement. These conditions may require specialized medical interventions, and it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and management.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Nerve Impingement
Certain lifestyle factors can also contribute to impingement of the greater auricular nerve. Prolonged pressure applied to the side of the head or neck, such as when sleeping on one side consistently, can lead to nerve compression over time.
If you notice persistent pain, numbness, or tingling in the area surrounding your ear, it is advisable to make changes in your sleeping position or use a supportive pillow to alleviate the pressure on the affected side. However, it is always important to seek medical advice to rule out any underlying medical conditions and receive appropriate treatment.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Greater Auricular Nerve Impingement
Impingement of the greater auricular nerve can cause various symptoms that can vary in severity and duration. It is important to be aware of these symptoms in order to seek appropriate medical attention.
Physical Symptoms
The physical symptoms associated with greater auricular nerve impingement may include pain, tenderness, and swelling in the side of the head and neck. The affected area may also feel warm or have a sensation of tightness or pressure.
In some cases, individuals may experience muscle weakness or difficulty moving their head or neck due to the impingement of the nerve. It is important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other underlying medical conditions, and a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Sensory Symptoms
One of the hallmark symptoms of greater auricular nerve impingement is sensory disturbances in the area supplied by the nerve. This can manifest as numbness, tingling, or an altered sensation in the skin overlying the ear and the mastoid region.
Sometimes, individuals may also experience an increased sensitivity or a heightened perception of pain in the affected area. It is essential to consult with a medical professional to determine the underlying cause of these symptoms and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Impact on Daily Life
Greater auricular nerve impingement can significantly impact a person’s daily life. The pain, discomfort, and sensory disturbances associated with this condition can interfere with routine activities, such as sleeping, working, or engaging in recreational pursuits.
If you find that your symptoms are affecting your quality of life or limiting your ability to perform daily tasks, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can assess your condition, provide guidance on managing your symptoms, and offer treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Diagnostic Procedures for Greater Auricular Nerve Impingement
Accurate diagnosis of greater auricular nerve impingement is crucial for appropriate treatment and management of symptoms. Healthcare professionals employ various diagnostic procedures to evaluate and confirm the presence of nerve impingement.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A detailed medical history and thorough physical examination are essential steps in the diagnostic process. Your healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms, medical history, and any recent injuries or trauma to the head or neck.
During the physical examination, your healthcare provider may perform specific tests to assess the sensory function of the affected area and evaluate for any signs of nerve impingement. These may include assessing your ability to feel light touch, sharp sensations, or changes in temperature in the skin overlying the ear and mastoid region.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, healthcare professionals may recommend imaging tests to further evaluate the underlying cause of greater auricular nerve impingement. Imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans can help identify any structural abnormalities, such as tumors or cysts, that may be contributing to nerve compression.
It is important to note that the decision to order imaging tests should be made by a healthcare professional based on the individual’s clinical presentation and specific needs.
Nerve Conduction Studies
In certain situations, nerve conduction studies may be performed to assess the function and integrity of the greater auricular nerve. These tests involve the placement of electrodes on the skin and the measurement of electrical activity transmitted through the nerve.
Nerve conduction studies can provide valuable information about the speed and amplitude of nerve impulses, helping to identify any abnormalities or disruptions in the nerve conduction pathway. However, it is important to note that these tests are typically performed by specialists and may not be necessary in all cases of nerve impingement.
In Conclusion
Impingement of the greater auricular nerve can cause significant discomfort and disrupt daily life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial in managing this condition effectively.
If you suspect that you may be experiencing impingement of the greater auricular nerve, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can evaluate your condition, provide accurate diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Remember, this article is for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have any concerns or questions regarding your health, it is always best to consult with a qualified healthcare professional.
Leave a Reply