The pre-auricular nerve is a critical component of the nervous system that plays a vital role in the functioning of the human body. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and potential disorders is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the pre-auricular nerve, explore associated disorders, and explore current treatment options.
An Overview of the Pre-Auricular Nerve
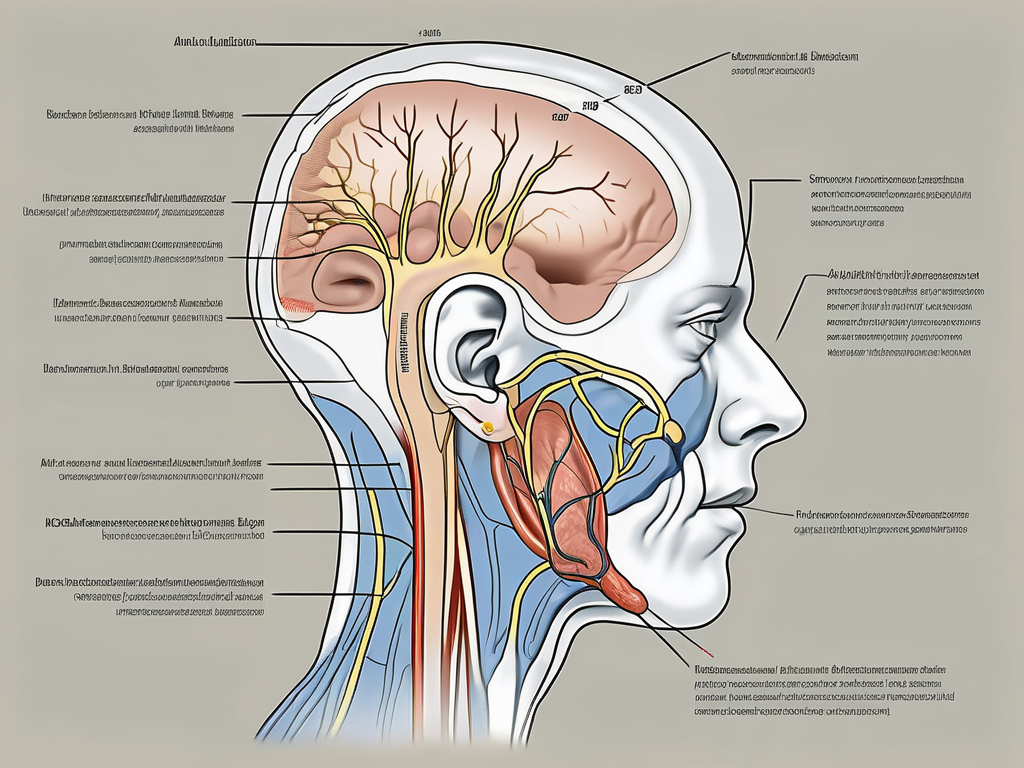
Before delving into the world of pre-auricular nerve disorders, it is important to establish a foundational understanding of the nerve itself. The pre-auricular nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, one of the major nerves in the head and neck region. It emerges near the temporomandibular joint and supplies sensation to the skin around the ear and temple area.
Anatomy and Location of the Pre-Auricular Nerve
The pre-auricular nerve travels alongside the superficial temporal artery, ultimately branching out to supply a designated area of the head. Its precise location can vary slightly between individuals, but it generally runs parallel to the ear, extending towards the temple region.
Understanding the precise anatomy and location of the pre-auricular nerve is crucial for medical professionals to accurately diagnose and treat potential disorders that may arise in this region.
The pre-auricular nerve can be visualized as a delicate network of nerve fibers, intricately woven through the surrounding tissues. It courses its way through the complex web of muscles, blood vessels, and connective tissues, ensuring the proper functioning of the sensory pathway.
As it travels alongside the superficial temporal artery, the pre-auricular nerve forms numerous connections and communicates with other nerves in the head and neck region. This intricate network of nerves allows for the transmission of sensory information and coordination of various bodily functions.
The Role of the Pre-Auricular Nerve in the Body
The pre-auricular nerve serves a vital sensory function, providing innervation to the skin around the ear and temple area. Its main role is to relay sensory information to the brain, allowing for the perception of touch, pain, and temperature in the designated areas.
Moreover, the pre-auricular nerve contributes to the overall functionality of the cranial nerves and works in conjunction with other nerves in the head and neck region to regulate various bodily functions.
When the pre-auricular nerve detects a stimulus, such as a gentle touch or a sharp pain, it sends electrical signals to the brain, which then processes and interprets the information. This intricate process allows us to be aware of our surroundings and respond accordingly.
Furthermore, the pre-auricular nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the head and neck region. It helps regulate blood flow, ensuring that the tissues receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients. Additionally, it aids in maintaining the temperature balance, allowing the body to adapt to different environmental conditions.
Overall, the pre-auricular nerve is a remarkable component of the intricate neural network in the head and neck region. Its sensory function and role in regulating bodily functions make it an essential part of our everyday lives, even though we may not always be aware of its presence.
Disorders Associated with the Pre-Auricular Nerve
While the pre-auricular nerve generally functions smoothly, it is susceptible to various disorders that may cause discomfort and affect daily life. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of pre-auricular nerve disorders is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment.
The pre-auricular nerve, also known as the auriculotemporal nerve, is a branch of the trigeminal nerve that supplies sensation to the skin of the temple, external ear, and the area in front of the ear. It plays a vital role in transmitting sensory information from these regions to the brain.
One common disorder associated with the pre-auricular nerve is trigeminal neuralgia. This condition is characterized by sudden, severe facial pain that can be triggered by simple activities such as eating, talking, or even touching the face. The pain is often described as electric shock-like and can be debilitating.
Common Symptoms of Pre-Auricular Nerve Disorders
Pre-auricular nerve disorders can manifest in various ways, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Common symptoms include sharp or shooting pain around the ear and temple area, abnormal sensations like tingling or numbness, and increased sensitivity to touch or temperature changes in the affected region.
In addition to these symptoms, some individuals may experience muscle weakness or twitching in the face, difficulty chewing or swallowing, and even changes in taste sensation. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making it essential to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other conditions, such as temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders or ear infections, so consulting with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis is necessary.
Diagnosing Pre-Auricular Nerve Disorders
Diagnosing pre-auricular nerve disorders requires a comprehensive evaluation conducted by a trained healthcare professional. Medical history assessment, physical examinations, and, in some cases, imaging tests and nerve conduction studies may be employed to determine the underlying cause of the symptoms.
During a physical examination, the healthcare provider may carefully assess the affected area, looking for any visible signs of inflammation or abnormalities. They may also perform specific tests to evaluate the nerve function and assess the extent of the damage.
In some cases, imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be ordered to obtain detailed images of the affected area. These imaging tests can help identify any structural abnormalities or lesions that may be causing the symptoms.
Nerve conduction studies, on the other hand, involve measuring the electrical activity of the nerves to assess their function. This test can help determine if there is any damage or dysfunction in the pre-auricular nerve or other related nerves.
To ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan, seeking medical advice from a qualified healthcare provider is essential. They will be able to evaluate the symptoms, perform the necessary tests, and recommend the most suitable treatment options based on the underlying cause of the pre-auricular nerve disorder.
Treatment Options for Pre-Auricular Nerve Disorders
Fortunately, various treatment options are available to manage pre-auricular nerve disorders effectively. It is crucial to explore both non-surgical and surgical interventions to determine the most suitable approach based on the severity and underlying cause of the disorder.
Non-Surgical Treatments and Therapies
Non-surgical interventions for pre-auricular nerve disorders may include medication to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation, physical therapy to improve muscle function and relieve tension, and alternative therapies such as acupuncture or nerve blocks.
However, the optimal treatment plan may vary for each individual, and it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most effective options tailored to specific needs.
Surgical Interventions for Pre-Auricular Nerve Disorders
In cases where non-surgical approaches do not provide sufficient relief, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical procedures can involve decompressing the nerve, removing any obstructions or lesions, or repairing damaged nerve sections.
Surgical interventions, while potentially beneficial for some individuals, carry certain risks and require careful consideration under the guidance of a skilled medical professional.
Living with a Pre-Auricular Nerve Disorder
Individuals living with a pre-auricular nerve disorder can experience challenges related to daily activities and overall quality of life. However, there are strategies to manage symptoms and improve well-being.
Managing Symptoms at Home
Self-care practices can play a crucial role in managing pre-auricular nerve disorder symptoms. Strategies such as applying heat or cold packs, practicing relaxation techniques, and avoiding triggers that exacerbate symptoms can provide relief and improve comfort.
However, it is important to note that self-care measures should complement, not replace, professional medical advice and treatment.
Long-Term Prognosis and Quality of Life
The long-term prognosis and quality of life for individuals with pre-auricular nerve disorders can vary depending on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and effectiveness of treatment. Prompt diagnosis, appropriate medical interventions, and diligent self-care efforts can positively impact prognosis and improve overall well-being.
It is crucial for individuals with pre-auricular nerve disorders to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their specific needs.
Future Research and Developments
Advances in medical research continue to foster promising developments in the understanding and treatment of pre-auricular nerve disorders.
Advances in Pre-Auricular Nerve Disorder Treatment
Researchers are actively exploring innovative treatment modalities such as nerve regeneration techniques, targeted drug therapy, and advanced diagnostic technologies to enhance accuracy and effectiveness in managing pre-auricular nerve disorders.
By staying informed about emerging research, individuals and healthcare professionals can stay abreast of the latest developments and potential future avenues for treatment.
The Future of Pre-Auricular Nerve Disorder Research
Continued research endeavors aimed at unraveling the complexities of pre-auricular nerve disorders can provide a deeper understanding of their underlying causes and mechanisms. Such research can pave the way for more effective diagnostic tools, personalized treatment approaches, and improved outcomes for individuals affected by these disorders.
Ultimately, developments in pre-auricular nerve disorder research hold immense promise for the future, offering hope for enhanced quality of life and improved management strategies.
In conclusion, understanding the pre-auricular nerve and its functions, disorders, and available treatments is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals affected by these conditions. By staying informed, seeking medical advice when necessary, and exploring the most appropriate treatment options, individuals can effectively manage pre-auricular nerve disorders and improve their overall well-being.
Leave a Reply