The posterior auricular nerve plays a crucial role in the functioning of the head and neck. Understanding this nerve and its functions is essential for medical professionals and individuals seeking to learn more about their own health. In this article, we will explore the anatomy of the posterior auricular nerve, its connection to the brain, its role in sensory and motor functions, disorders related to the nerve, and its potential implications in pain management and future research directions.
Understanding the Posterior Auricular Nerve
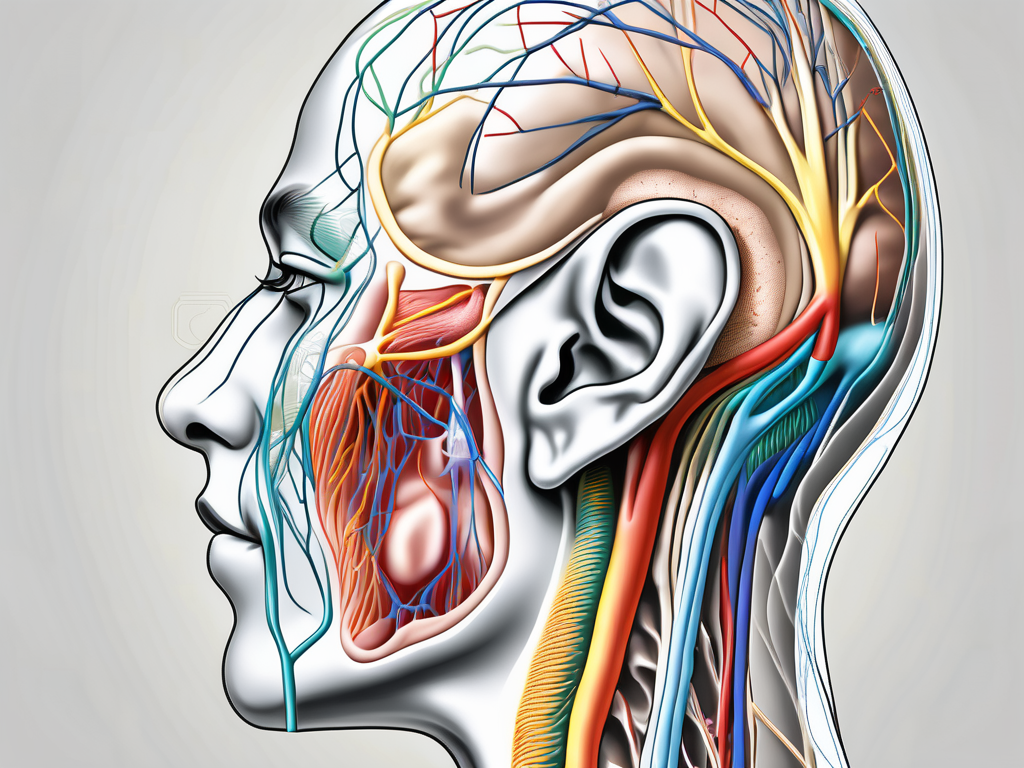
The posterior auricular nerve is a branch of the facial nerve, also known as cranial nerve VII. It emerges from the mastoid process, a bony prominence located behind the ear. From there, it branches out to supply various regions of the head and neck, including the area behind the ear, the skin above the ear, and parts of the scalp.
The posterior auricular nerve plays a crucial role in the sensory and motor functions of the head and neck. Let’s delve deeper into its anatomy and its connection to the brain.
Anatomy of the Posterior Auricular Nerve
The posterior auricular nerve consists of sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers transmit signals from the skin back to the brain, allowing us to perceive touch, temperature, and pain in the innervated areas. These fibers are responsible for the exquisite sensitivity of the skin behind the ear and the scalp, allowing us to feel even the slightest touch or change in temperature.
On the other hand, the motor fibers of the posterior auricular nerve control the movement of specific muscles. These muscles are essential for facial expressions, such as raising the eyebrows or wrinkling the forehead. The coordinated action of these muscles allows us to convey various emotions and communicate non-verbally.
The Nerve’s Connection to the Brain
The posterior auricular nerve is connected to the brain through the cranial nerve VII, also known as the facial nerve. This connection is vital for the nerve’s function in both motor and sensory capacities.
The facial nerve receives signals from the brain, allowing it to deliver motor commands to the muscles it innervates. This intricate system of nerve signals and muscle contractions enables us to make countless facial expressions, from smiling and frowning to winking and raising our eyebrows.
Additionally, the sensory fibers of the posterior auricular nerve transmit information back to the brain. This feedback provides vital information about the external environment and potential threats. For example, if a mosquito lands on the skin behind the ear, the sensory fibers of the posterior auricular nerve quickly send a signal to the brain, prompting a reflex action to swat away the insect.
Moreover, the sensory feedback from the posterior auricular nerve helps us maintain our balance and spatial orientation. It provides important information about the position of our head and neck in relation to the environment, allowing us to navigate our surroundings with precision and stability.
Understanding the intricate details of the posterior auricular nerve enhances our appreciation for the complexity and sophistication of the human body. From its role in sensation to its contribution to facial expressions, this nerve plays a crucial part in our daily lives, often without us even realizing it.
The Role of the Posterior Auricular Nerve
The posterior auricular nerve serves significant functions in sensory perception and motor control. Let’s explore these functions in more detail:
Sensory Functions
The sensory fibers of the posterior auricular nerve play a crucial role in our ability to perceive touch, temperature, and pain in the areas they innervate. This allows us to react appropriately to stimuli and protect ourselves from potential harm.
When the posterior auricular nerve detects a gentle touch, it sends signals to the brain, which interprets the sensation as a soft caress. This can trigger feelings of comfort and relaxation, promoting a sense of well-being. On the other hand, if the nerve detects a sharp pain, it quickly transmits signals to the brain, alerting us to potential danger. This rapid response helps us withdraw from harmful stimuli and avoid injury.
In addition to touch and pain perception, the posterior auricular nerve also contributes to our ability to sense temperature. When exposed to a cold environment, the nerve’s sensory fibers detect the change in temperature and send signals to the brain. This prompts the body to initiate physiological responses, such as shivering or seeking warmth, to maintain a stable internal temperature.
Motor Functions
The motor fibers of the posterior auricular nerve control the movement of specific muscles in the head and neck region. These muscles are responsible for facial expressions, such as raising the eyebrows, wrinkling the forehead, and moving the ears. The nerve’s motor functions contribute significantly to our ability to communicate non-verbally and express emotions.
When we are surprised or intrigued, the posterior auricular nerve activates the muscles that raise our eyebrows. This movement helps convey our emotions and can indicate interest or curiosity. Similarly, when we furrow our forehead, the nerve’s motor fibers are responsible for this action. This expression often signifies concentration or concern.
Interestingly, the posterior auricular nerve also plays a role in the movement of our ears. While humans do not possess the same level of ear mobility as some animals, the nerve’s motor fibers still contribute to subtle movements. These movements can occur in response to auditory stimuli or as a reflexive response to certain emotions, such as fear or surprise.
In conclusion, the posterior auricular nerve is not only responsible for sensory perception but also plays a crucial role in our ability to express emotions through facial expressions. Its sensory functions allow us to perceive touch, temperature, and pain, while its motor functions enable us to raise our eyebrows, wrinkle our forehead, and subtly move our ears. The intricate workings of this nerve contribute to our overall sensory experience and non-verbal communication abilities.
Disorders Related to the Posterior Auricular Nerve
Like any other nerve, the posterior auricular nerve can be affected by various disorders. It’s essential to recognize the symptoms of dysfunction and seek proper diagnosis and treatment options. However, please note that the information provided here is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
The posterior auricular nerve, also known as the great auricular nerve, is a branch of the facial nerve. It provides sensory innervation to the skin overlying the mastoid process and the auricle, the external part of the ear. When this nerve is affected by disorders, it can lead to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life.
Symptoms of Dysfunction
When the posterior auricular nerve is dysfunctional, it can lead to various symptoms, including pain, numbness, tingling sensations, and muscle weakness in the affected areas. These symptoms may affect daily activities and quality of life.
The pain associated with posterior auricular nerve dysfunction can vary in intensity, ranging from mild discomfort to severe, sharp, shooting pain. It may be localized to the area behind the ear or radiate to other parts of the head and neck. Numbness and tingling sensations can also be present, causing a loss of sensation or abnormal sensations like pins and needles. Muscle weakness may affect the muscles responsible for facial expressions or the muscles surrounding the ear, leading to difficulties in movements.
It’s important to note that the symptoms experienced may vary from person to person, depending on the underlying cause of the dysfunction. Some individuals may only experience mild discomfort, while others may have more severe symptoms that significantly impact their daily lives.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. They may perform a thorough physical examination, review your medical history, and order additional tests or imaging studies to determine the underlying cause of the dysfunction.
During the physical examination, the healthcare professional may assess the affected area for any visible signs of inflammation, tenderness, or swelling. They may also evaluate the range of motion and strength of the muscles surrounding the ear and the face. Additionally, they may perform sensory tests to assess any loss of sensation or abnormal sensations.
Depending on the suspected cause of the dysfunction, further tests may be ordered. These can include blood tests to check for any underlying systemic conditions, nerve conduction studies to assess the nerve’s function, or imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize the structures in the affected area.
Treatment options for posterior auricular nerve dysfunction may vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. In some cases, conservative measures such as pain medications, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physical therapy may be recommended to alleviate symptoms and improve function.
In more severe cases, nerve blocks or injections of local anesthetics or corticosteroids may be used to target the affected nerve and provide temporary relief. Surgical interventions, such as decompression or repair of the nerve, may be considered in rare cases where conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief.
It’s important to remember that each individual’s situation is unique, and treatment recommendations should be personalized based on their specific needs and circumstances. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to receive accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
The Posterior Auricular Nerve and Pain Management
Chronic pain can significantly impact an individual’s well-being and quality of life. Understanding the role of the posterior auricular nerve in pain perception can open new possibilities for pain management techniques.
The Nerve’s Role in Chronic Pain
Recent research suggests that the posterior auricular nerve may play a role in chronic pain conditions, such as trigeminal neuralgia, occipital neuralgia, and migraines. Targeting this nerve through interventional techniques has shown promise in alleviating pain and improving the quality of life for individuals suffering from these conditions.
Interventional Techniques for Pain Relief
Various interventional techniques can be employed to target the posterior auricular nerve for pain relief. These techniques include nerve blocks, such as local anesthetic injections or radiofrequency ablation. However, it’s crucial to consult with a pain management specialist to determine the most appropriate course of action based on your specific condition.
Future Research Directions
While significant progress has been made in understanding the role and functions of the posterior auricular nerve, many questions remain unanswered. Ongoing research aims to uncover further insights into this fascinating nerve and its potential implications for various neurological disorders.
Unanswered Questions about the Posterior Auricular Nerve
Researchers are still investigating the precise innervation patterns and connections of the posterior auricular nerve. Additionally, they seek to elucidate the mechanisms underlying its role in sensory perception and motor control. Further research is also needed to explore potential therapeutic interventions for disorders affecting this nerve.
Potential Implications for Neurological Disorders
Understanding the posterior auricular nerve’s role and functions may have implications for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of various neurological disorders. Research in this area could pave the way for innovative therapeutic options and improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the posterior auricular nerve plays a vital role in sensory perception and motor control in the head and neck region. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and potential implications in pain management and neurological disorders is crucial for medical professionals and individuals seeking to enhance their knowledge. If you experience any symptoms related to the posterior auricular nerve, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment options.
Leave a Reply