The posterior auricular nerve is a vital component of the human nervous system with a significant role in sensory perception and facial expressions. By exploring the anatomy, function, and potential disorders related to this nerve, we can gain a deeper understanding of its importance and impact on our overall wellness.
Anatomy of the Posterior Auricular Nerve
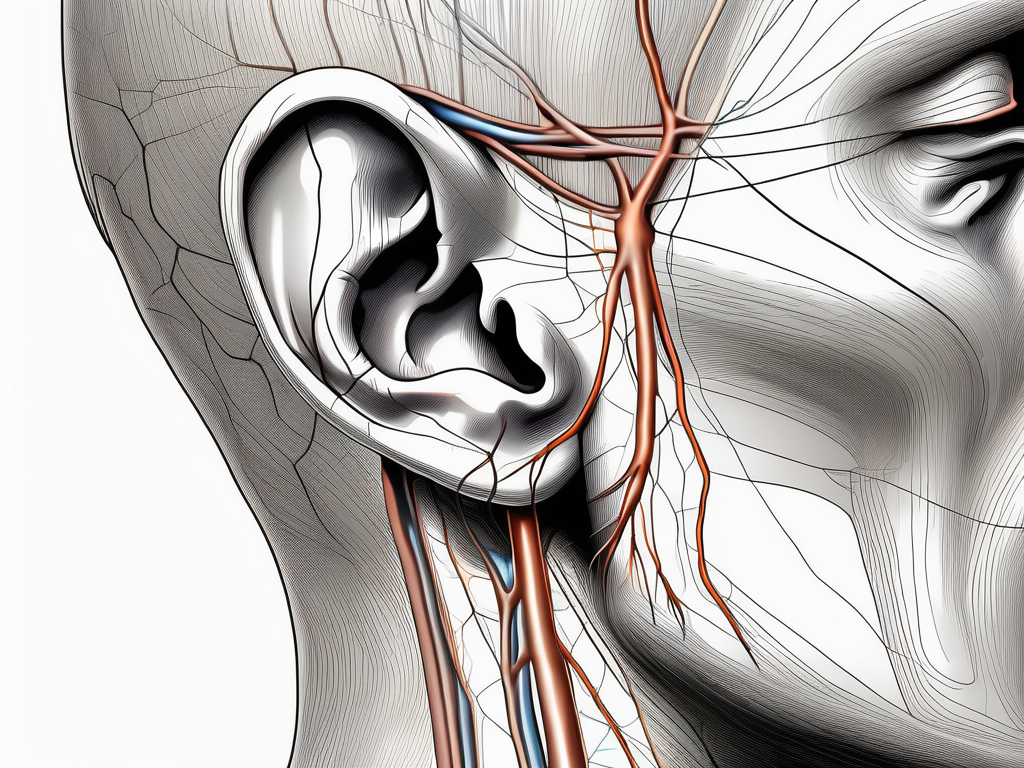
The posterior auricular nerve is a fascinating component of the facial nerve, with a complex origin and pathway. It plays a crucial role in the intricate network of nerves that control the muscles of facial expression and transmit sensory information from the ear and surrounding areas.
The posterior auricular nerve originates from the facial nerve, specifically from the angle of the facial canal. This angle, located within the temporal bone, serves as the starting point for the journey of the posterior auricular nerve. From here, it embarks on a remarkable pathway, coursing along the posterior aspect of the ear, towards the area behind the auricle.
Origin and Pathway
As a branch of the facial nerve, the posterior auricular nerve emerges from the angle of the facial canal. This canal, nestled within the temporal bone, is a narrow passageway that houses the facial nerve and its intricate branches. It is within this hidden realm that the posterior auricular nerve begins its journey.
From the angle of the facial canal, the posterior auricular nerve embarks on a remarkable course. It travels along the posterior aspect of the ear, navigating through the intricate layers of tissue and fascia. Its path is not a simple straight line, but rather a meandering route that allows it to reach its destination – the area behind the auricle.
Branches and Connections
Once it reaches the area behind the auricle, the posterior auricular nerve undergoes a fascinating transformation. It splits into several branches, each with its own unique purpose and destination. These branches form connections with nearby nerves, such as the great auricular nerve and the cervical branch of the facial nerve.
The interconnections between the posterior auricular nerve and these neighboring nerves create a complex network that facilitates communication between various sensory and motor pathways. This intricate web of nerves allows for the transmission of signals related to both sensation and movement, ensuring the proper functioning of the ear and surrounding structures.
Furthermore, the posterior auricular nerve’s branches extend beyond the area behind the auricle, reaching into adjacent regions. These branches contribute to the extensive functional capabilities of the posterior auricular nerve, allowing it to play a vital role in various processes, such as facial expression and sensory perception.
In conclusion, the posterior auricular nerve is a remarkable component of the facial nerve, with a complex origin, pathway, and interconnections. Its intricate journey and extensive branching contribute to its essential role in controlling facial expression and transmitting sensory information from the ear and surrounding areas.
Role of the Posterior Auricular Nerve in Sensory Perception
The posterior auricular nerve plays a crucial role in our ability to perceive different sensory stimuli, primarily those related to hearing and balance.
Sensing Sound Vibrations
One of the key functions of the posterior auricular nerve is to transmit sound vibrations from the external ear to the brain. This process allows us to interpret and comprehend the sounds we encounter in our environment. However, it is important to note that the nerve itself does not influence the quality or clarity of the sound perceived, as this mostly depends on other components of the auditory system.
When sound waves enter the external ear, they travel through the ear canal and reach the eardrum. The eardrum vibrates in response to these sound waves, which in turn sets the chain of events in motion. The posterior auricular nerve, along with other branches of the facial nerve, carries these vibrations to the brain for processing.
Once the sound vibrations reach the brain, they are interpreted by specialized areas such as the auditory cortex. This allows us to recognize and distinguish different sounds, whether it’s the melody of a song, the chirping of birds, or the sound of a car horn.
Role in Balance and Spatial Orientation
In addition to sound perception, the posterior auricular nerve contributes to our sense of balance and spatial orientation. By collecting sensory information from the inner ear, particularly the vestibular apparatus, the nerve aids in our ability to maintain equilibrium and coordinate movements.
The vestibular apparatus, located within the inner ear, consists of the utricle, saccule, and semicircular canals. These structures are responsible for detecting changes in head position and movement. When we tilt our heads, turn, or move in any direction, the vestibular apparatus sends signals to the brain through the posterior auricular nerve.
These signals are crucial for our brain to accurately perceive our body’s position in space. They help us maintain balance while walking, running, or even standing still. The posterior auricular nerve plays a vital role in this process by relaying the information from the vestibular apparatus to the brain, allowing us to navigate our surroundings with precision and stability.
Furthermore, the posterior auricular nerve also interacts with other sensory systems, such as the visual system, to enhance our spatial orientation. The integration of information from multiple sensory modalities helps us create a comprehensive understanding of our environment and enables us to move and interact with it effectively.
The Posterior Auricular Nerve and Facial Expressions
Facial expressions are an integral part of human communication and emotional expression. They allow us to convey a wide range of emotions, from joy and happiness to sadness and anger. But have you ever wondered how our facial muscles work together to create these expressions? One crucial player in this intricate process is the posterior auricular nerve.
The posterior auricular nerve, also known as the great auricular nerve, is a branch of the facial nerve. It originates from the main trunk of the facial nerve and travels behind the ear, supplying sensation to the skin on the back of the ear and the area just above it. However, its role goes beyond providing sensory input.
Connection with Facial Muscles
The posterior auricular nerve establishes connections with various facial muscles, contributing to the coordination and control of facial movements. One of these connections is with the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, which is responsible for opening the mouth and depressing the mandible. This connection allows the nerve to transmit signals for movement and contractility, enabling us to perform actions like chewing and speaking.
Another significant connection is with the occipital belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle, also known as the epicranius muscle. This muscle plays a crucial role in facial expressions, particularly in raising the eyebrows and wrinkling the forehead. The posterior auricular nerve’s connection with this muscle allows it to facilitate these movements, adding depth and nuance to our expressions.
Impact on Facial Symmetry
An intact and properly functioning posterior auricular nerve is essential for maintaining facial symmetry. When both sides of the face work harmoniously, our expressions appear balanced and natural. However, any impairment or damage to the nerve can lead to asymmetric facial movements.
Facial asymmetry can manifest in various ways, such as a drooping corner of the mouth or uneven raising of the eyebrows. These asymmetries can affect our ability to convey emotions effectively, as they may not accurately reflect our true feelings. It can also impact our self-confidence and how others perceive us.
If you notice any facial asymmetry or abnormalities, it is crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can evaluate your condition and determine the underlying cause. Treatment options may include physical therapy, medication, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
So, the next time you smile, frown, or raise an eyebrow, remember the intricate role played by the posterior auricular nerve. It is a testament to the complexity and beauty of human anatomy, allowing us to express ourselves and connect with others on a deeper level.
Disorders Related to the Posterior Auricular Nerve
While the posterior auricular nerve usually functions optimally, there are certain conditions that can affect its performance, leading to various symptoms and challenges.
Causes and Symptoms
Disorders related to the posterior auricular nerve can arise from a variety of causes, such as trauma, infections, or underlying medical conditions. Symptoms may include pain behind the ear, tenderness, numbness, tingling sensations, and even facial weakness. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is vital to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Diagnostic Procedures
To determine the cause and extent of posterior auricular nerve disorders, healthcare professionals may employ various diagnostic procedures. These may include physical examinations, imaging studies, nerve conduction studies, and electromyography. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing effective treatment plans tailored to each individual’s needs.
Treatment Options for Posterior Auricular Nerve Disorders
The treatment of posterior auricular nerve disorders is multifaceted and depends on the underlying cause, severity, and individual circumstances. Treatment options may include both non-invasive approaches and surgical interventions.
Medication and Physical Therapy
Non-invasive treatment methods, such as the administration of pain medications, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physical therapy, may be recommended to manage pain, reduce inflammation, and restore optimal nerve function. Physical therapy modalities, including exercises, manual techniques, and therapeutic modalities, can help improve muscular strength, flexibility, and overall mobility.
Surgical Interventions
In certain cases where conservative management fails to provide sufficient relief, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical procedures can address underlying issues, such as nerve compression or injury, to restore optimal nerve function. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to discuss the potential risks, benefits, and expected outcomes of surgical interventions.
In conclusion, the posterior auricular nerve plays a significant role in sensory perception, facial expressions, and overall well-being. Understanding its anatomy, function, and potential disorders can help individuals recognize the importance of seeking medical evaluation and treatment when experiencing any abnormalities or symptoms related to this vital nerve. If you have concerns about your posterior auricular nerve or experience any related symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate assessment and guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Leave a Reply