Have you ever experienced a sharp, throbbing pain in your ear that seems to radiate towards your jaw or neck? If so, you may be suffering from a greater auricular nerve earache. Understanding the causes and treatment options for this condition is crucial in finding relief and improving your overall quality of life.
Anatomy of the Greater Auricular Nerve
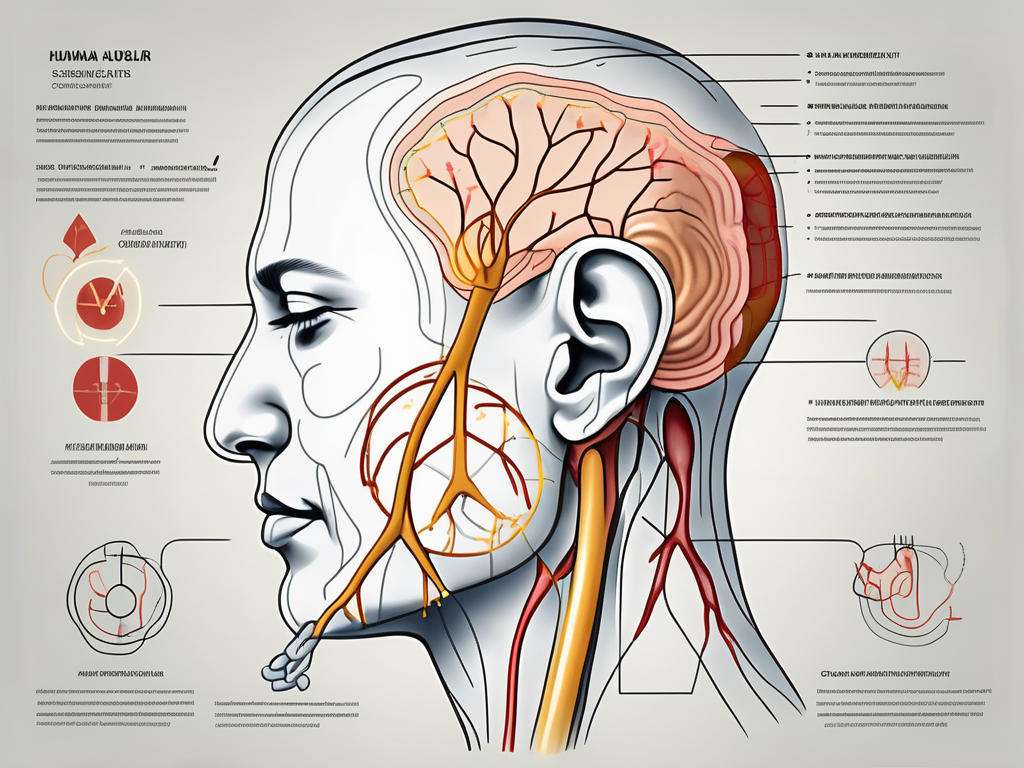
The greater auricular nerve is a peripheral nerve that originates from the cervical plexus, specifically from the spinal nerves C2 and C3. It is a sensory nerve that supplies the skin over the external ear and the area just below and behind it.
The nerve emerges from the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and extends upward, crossing the external jugular vein, before dividing into branches to supply the designated areas.
As the greater auricular nerve courses through the neck, it travels alongside other important structures such as the internal jugular vein and the carotid artery. This close proximity highlights the intricate nature of the human anatomy and the delicate balance required for proper nerve function.
Furthermore, the greater auricular nerve is part of a larger network of nerves known as the cervical plexus. This network is responsible for innervating various regions of the neck and head, ensuring that sensory information is transmitted accurately and efficiently.
The Role of the Greater Auricular Nerve in the Body
The greater auricular nerve plays a crucial role in providing sensory information to the skin it innervates. It allows us to feel touch, temperature, and pain in the specified areas.
Moreover, the greater auricular nerve is involved in the complex process of thermoregulation. It helps the body maintain a stable internal temperature by relaying information about external temperature changes to the brain, which then initiates appropriate responses to keep the body in homeostasis.
Additionally, this nerve plays a role in maintaining the proper functioning of the lymphatic system, as it carries lymphatic vessels that drain the lymphatic fluid from the skin it supplies. This function is essential for immune response and the removal of waste products from the body.
The Connection Between the Greater Auricular Nerve and the Ear
The greater auricular nerve is closely connected to the ear. It supplies the skin over the external ear, including the auricle and the area behind it. When this nerve is affected or damaged, it can lead to earache and other associated symptoms.
It’s important to note that although the greater auricular nerve supplies the skin of the ear, it does not have a direct connection to the structures within the ear, such as the ear canal or the middle and inner ear. Therefore, a greater auricular nerve earache does not usually indicate an issue with those structures.
However, the close relationship between the greater auricular nerve and the ear highlights the interconnectedness of the human body. The intricate network of nerves, blood vessels, and tissues work together to ensure the proper functioning of various body parts, including the ear.
Furthermore, the greater auricular nerve’s proximity to the ear makes it susceptible to injury or compression. This can occur due to trauma, prolonged pressure, or certain medical conditions. Understanding the anatomy of this nerve can help healthcare professionals diagnose and treat conditions affecting the ear and the surrounding areas.
Identifying the Symptoms of Greater Auricular Nerve Earache
If you suspect that you may be experiencing a greater auricular nerve earache, it’s essential to identify the specific symptoms associated with this condition.
A greater auricular nerve earache can be a distressing experience, causing a range of physical and emotional symptoms that can significantly impact your daily life. Understanding these symptoms can help you seek appropriate treatment and support.
Physical Symptoms
Common physical symptoms include sharp, shooting ear pain that may radiate towards the jaw or neck. This pain can be intense and debilitating, making it difficult to concentrate or engage in regular activities. The affected area may also become sensitive to touch, making it uncomfortable to wear headphones or even rest your head on a pillow. In some cases, you may experience numbness or tingling sensations, adding to the discomfort.
Furthermore, the pain caused by a greater auricular nerve earache can lead to muscle tension and stiffness in the surrounding areas. This can result in headaches, jaw pain, and neck pain, further adding to the overall discomfort and distress.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Living with a greater auricular nerve earache can have a significant impact on your emotional well-being. The constant pain and discomfort can lead to frustration, irritability, and even anxiety or depression. The persistent nature of the pain can make it challenging to find relief, causing feelings of hopelessness and despair.
Additionally, the physical limitations imposed by the earache can restrict your ability to participate in social activities or enjoy hobbies, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness. It is not uncommon for individuals with a greater auricular nerve earache to experience a decrease in their overall quality of life.
Seeking support from loved ones and considering professional counseling may be beneficial in managing these emotional and psychological effects. Talking to a therapist can provide you with coping strategies and a safe space to express your feelings and frustrations.
In conclusion, a greater auricular nerve earache can cause a range of physical and emotional symptoms that can significantly impact your well-being. By understanding these symptoms and seeking appropriate support, you can better manage the challenges associated with this condition.
Common Causes of Greater Auricular Nerve Earache
Now that we understand the anatomy and symptoms associated with a greater auricular nerve earache, let’s explore some of the common causes of this condition.
Infections and Inflammations
One of the primary causes of a greater auricular nerve earache is infections or inflammations in the surrounding areas. Conditions such as otitis externa (swimmer’s ear) or cellulitis can lead to irritation and compression of the nerve, resulting in ear pain.
If you suspect an infection or inflammation, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can properly diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Trauma and Injuries
Any trauma or injury to the area where the greater auricular nerve runs can lead to earache. This includes accidents, falls, or surgeries in the neck or ear region. It’s important to be cautious and seek medical attention if you experience severe trauma to these areas.
Chronic Conditions and Diseases
Certain chronic conditions and diseases can also contribute to the development of a greater auricular nerve earache. Conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and tumors can cause nerve damage or compression, resulting in pain and discomfort.
If you have an existing chronic condition, it is essential to manage it effectively to minimize the risk of complications and associated earaches. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial for maintaining overall health.
Diagnostic Procedures for Greater Auricular Nerve Earache
If you are experiencing a greater auricular nerve earache, a healthcare professional will perform various diagnostic procedures to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your healthcare provider will start by taking a detailed medical history, including any previous ear or neck injuries, existing medical conditions, and a thorough examination to evaluate the affected area.
They may gently touch the skin of the ear, neck, and other areas supplied by the greater auricular nerve to assess sensitivity and pain response. This examination helps in ruling out other potential causes of your symptoms.
Imaging and Laboratory Tests
In some cases, your healthcare provider may order imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to assess the structures in the surrounding areas and identify any abnormalities or signs of inflammation. Laboratory tests may also be performed to check for any underlying infections or specific markers associated with certain conditions.
These diagnostic procedures help in confirming the diagnosis and determining the most appropriate treatment plan for your greater auricular nerve earache.
Treatment Options for Greater Auricular Nerve Earache
Once a diagnosis has been made, your healthcare provider will discuss suitable treatment options for your greater auricular nerve earache. It’s important to note that the treatment approach may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of your symptoms.
Medications and Drugs
In many cases, medications can provide relief from the pain and inflammation associated with a greater auricular nerve earache. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics may be prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
Your healthcare provider may also recommend topical medications or ear drops to target the area directly and provide localized relief.
It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions carefully. If over-the-counter medications are being used, consult with a healthcare professional to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your condition.
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy and specific exercises can be beneficial in managing a greater auricular nerve earache. Your healthcare provider may refer you to a physical therapist who can guide you through exercises and techniques to improve the flexibility and strength of the affected areas.
These exercises can help alleviate pain, decrease muscle tension, and promote overall healing and recovery.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical options may include decompression of the nerve, removal of any tumor or abnormal growth, or other procedures aimed at alleviating compression on the greater auricular nerve.
It’s important to have an open discussion with your healthcare provider about the potential risks, benefits, and expected outcomes of any surgical intervention. They will guide you in making an informed decision based on your specific circumstances.
Remember, this article is intended to provide general information about the causes and treatment options of a greater auricular nerve earache. It is not medical advice, and the information should not replace consultation with a healthcare professional. If you are experiencing ear pain or any concerning symptoms, seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider who can assess your individual situation and provide appropriate recommendations for your care.
Leave a Reply