The Greater Auricular Nerve, also known as the Auriculotemporal Nerve, is a nerve that plays a crucial role in the sensation of the ear and the area around it. It is important to understand the anatomy and function of this nerve, as well as the concept of nerve burning, its associated risks and benefits, and the feasibility of burning the Greater Auricular Nerve. Additionally, post-procedure care and recovery are key aspects to consider. It is essential to approach any medical procedure with caution and seek professional advice when exploring treatment options.
Understanding the Greater Auricular Nerve
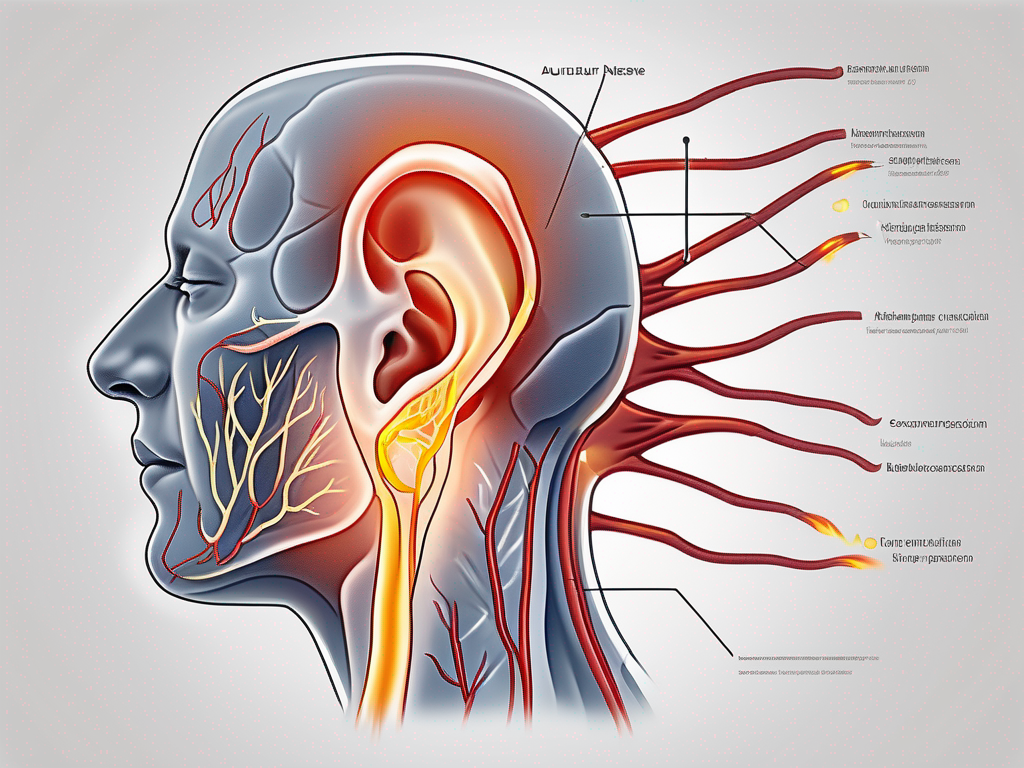
The Greater Auricular Nerve is a sensory branch of the cervical plexus that originates from the second and third cervical nerves. It supplies sensation to the skin over the ear, the area behind the ear, and the angle of the mandible. This nerve is responsible for transmitting sensory information, allowing us to feel touch, pain, and temperature in these specific areas.
Anatomy and Function of the Greater Auricular Nerve
The Greater Auricular Nerve consists of afferent sensory fibers that originate from the spinal cord and transmit signals to the brain. It travels superficially along the side of the neck, passing over the sternocleidomastoid muscle, before branching out to innervate the designated areas.
As the nerve travels along the neck, it is accompanied by small blood vessels that provide nourishment to the nerve fibers. These blood vessels ensure the proper functioning of the nerve and help maintain its integrity.
The Greater Auricular Nerve plays a crucial role in our daily lives. It allows us to perceive the sensation of touch, enabling us to feel the gentle brush of a breeze against our ear or the warmth of the sun on our skin. It also helps us detect pain, warning us of potential harm or injury. Additionally, the nerve enables us to sense changes in temperature, ensuring that we can adapt to our environment and protect ourselves from extreme heat or cold.
Common Disorders and Injuries of the Greater Auricular Nerve
Like any other nerve, the Greater Auricular Nerve can be subject to various disorders and injuries. These may include compression, entrapment, or trauma. Nerve entrapment can result from chronic postural habits or direct pressure from external factors. For example, individuals who frequently rest their head on their hands or wear tight headbands may experience compression of the nerve, leading to discomfort or altered sensation in the affected areas.
Injuries to the Greater Auricular Nerve can occur due to accidents or surgical procedures involving the head, ear, or neck area. Trauma to the nerve can result in temporary or permanent loss of sensation, depending on the severity of the injury. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain in the areas supplied by the Greater Auricular Nerve.
Fortunately, the Greater Auricular Nerve has the ability to regenerate and repair itself to some extent. With proper medical care and rehabilitation, individuals with nerve injuries can often regain sensation and function in the affected areas over time.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the Greater Auricular Nerve can help us appreciate the intricate network of nerves that enable us to experience the world around us. From the gentle touch of a loved one’s hand on our ear to the warning signals of pain, our nerves play a vital role in our everyday experiences. So next time you feel the breeze against your ear or the warmth of the sun on your skin, take a moment to thank your Greater Auricular Nerve for allowing you to perceive these sensations.
The Concept of Nerve Burning
Nerve burning, also known as neurolysis or radiofrequency ablation, is a medical procedure that involves using heat to selectively destroy specific nerve fibers. The purpose is to alleviate pain or reduce the transmission of pain signals from the affected nerve.
Nerve burning refers to the targeted destruction of nerve fibers using techniques such as heat or radiofrequency waves. The aim is to interrupt pain signals from reaching the brain, providing relief to individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions.
Chronic pain can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, affecting their ability to perform daily activities and causing emotional distress. Nerve burning procedures offer a potential solution for those who have not found relief from other treatment options.
What Does Nerve Burning Mean?
Nerve burning, also known as neurolysis or radiofrequency ablation, is a minimally invasive procedure that targets specific nerves to alleviate pain. It involves the use of heat or radiofrequency waves to selectively destroy nerve fibers, interrupting the transmission of pain signals to the brain.
During the nerve burning procedure, a thin needle or electrode is inserted near the targeted nerve under the guidance of imaging techniques such as fluoroscopy or ultrasound. Once the needle is in place, heat or radiofrequency waves are applied to the nerve, creating a lesion that disrupts the transmission of pain signals.
The duration of the procedure may vary depending on the complexity of the case and the number of nerves being treated. In some cases, multiple nerves may need to be targeted to provide optimal pain relief.
Medical Procedures Involving Nerve Burning
Nerve burning can be performed using various techniques, including radiofrequency ablation and chemical neurolysis. These procedures are typically carried out by qualified healthcare professionals in a controlled medical setting.
Radiofrequency ablation involves the use of high-frequency electrical currents to generate heat and destroy targeted nerve fibers. This technique has been shown to be effective in providing long-term pain relief for conditions such as chronic back pain, arthritis, and neuropathic pain.
Chemical neurolysis, on the other hand, involves the injection of a chemical agent, such as alcohol or phenol, directly into the targeted nerve. The chemical agent destroys the nerve fibers, providing pain relief. This technique is often used for smaller nerves or when radiofrequency ablation is not suitable.
Before undergoing a nerve burning procedure, patients will typically undergo a thorough evaluation to determine the appropriateness of the treatment. This may include a review of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as imaging studies or nerve blocks.
It is important to note that nerve burning procedures are not without risks. Potential complications may include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, or allergic reactions to the medications used during the procedure. Therefore, it is crucial for patients to discuss the potential benefits and risks with their healthcare provider before making a decision.
In conclusion, nerve burning, or neurolysis, is a medical procedure that involves the targeted destruction of nerve fibers using heat or radiofrequency waves. It is a minimally invasive option for individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions who have not found relief from other treatment options. However, it is important to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and discuss the procedure thoroughly with a healthcare professional.
Risks and Benefits of Nerve Burning
As with any medical procedure, nerve burning carries potential risks and benefits. It is important to weigh these factors before considering this treatment option.
Potential Risks and Complications
While nerve burning may offer pain relief, it is crucial to be aware of potential risks and complications. These can include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and transient or permanent loss of sensation in the treated area. It is vital to consult with a healthcare professional to evaluate individual risks and determine if nerve burning is appropriate.
Therapeutic Benefits and Success Rates
Nerve burning can provide therapeutic benefits for patients suffering from chronic pain conditions. Success rates vary depending on the individual and the specific medical condition. It is essential to have open discussions with healthcare professionals regarding treatment expectations.
The Feasibility of Burning the Greater Auricular Nerve
When considering nerve burning for the Greater Auricular Nerve, medical opinions and research findings come into play. This, combined with patient considerations and alternative treatment options, can help determine if burning the Greater Auricular Nerve is a feasible solution.
Medical Opinions and Research Findings
Medical opinions and research findings regarding nerve burning for the Greater Auricular Nerve are still evolving. It is crucial to consult with specialists or healthcare providers experienced in the field to assess whether this treatment modality is suitable for individual cases.
Patient Considerations and Alternatives
Each patient is unique, and there may be alternative treatment options available for managing conditions related to the Greater Auricular Nerve. It is essential to discuss all feasible alternatives, potential risks, and expected outcomes with healthcare professionals to make informed decisions.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
After nerve burning, post-procedure care and recovery are fundamental aspects for optimal healing and preventing future issues.
What to Expect After Nerve Burning
Following nerve burning, patients may experience temporary discomfort, swelling, or bruising in the treated area. It is important to adhere to any specific post-procedure instructions provided by the healthcare professional, such as avoiding strenuous activities and keeping the area clean and dry to promote healing.
Tips for a Smooth Recovery and Prevention of Future Issues
To ensure a smooth recovery and minimize the risk of future problems, patients should follow post-procedure care guidelines provided by their healthcare professional. This may include medications, physical therapy exercises, and regular follow-up appointments.In conclusion, the concept of burning the Greater Auricular Nerve is a specialized medical procedure that should only be undertaken after careful consideration and consultation with a healthcare professional. While nerve burning may offer potential pain relief benefits, it is essential to understand the associated risks, treatment alternatives, and post-procedure care for a successful and smooth recovery. Always seek expert medical advice to explore the most appropriate treatment options for individual circumstances.
Leave a Reply